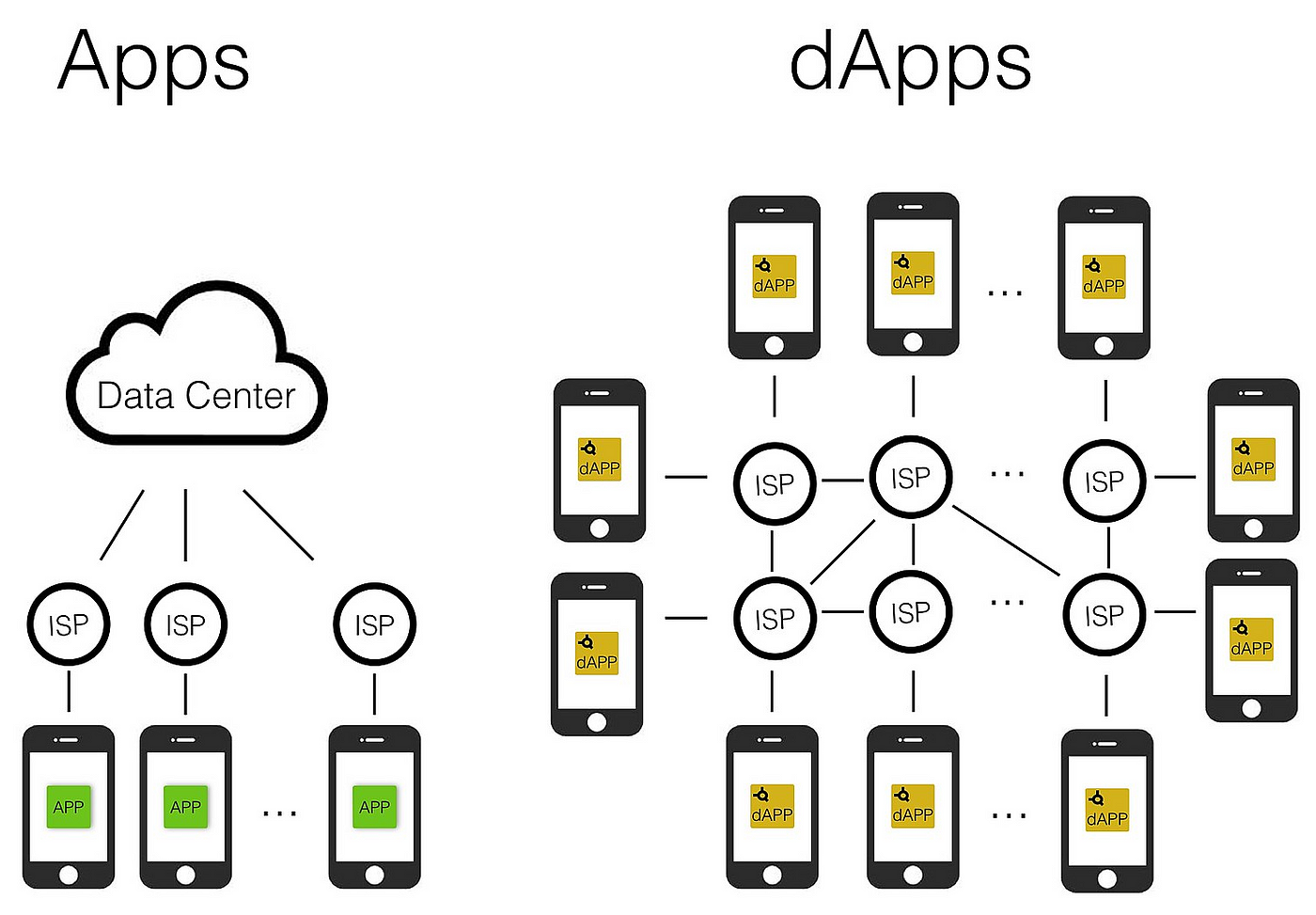
Decentralized applications, or dApps, are software programs that run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers instead of on a single computer. DApps (also called “dapps”) are thus outside the purview and control of a single authority.
DApps are often built on the Ethereum platform. They have been developed for a variety of purposes including gaming, finance, and social media.
Key Points
- Decentralized applications—also known as “dApps” or “dapps”—are digital applications that run on a blockchain network of computers instead of relying on a single computer.
- dApps are free from the control and interference of a single authority.
- The benefits of dApps include the safeguarding of user privacy, the lack of censorship, and the flexibility of development.
- Potential drawbacks include an inability to scale, challenges in developing a user interface, and difficulties in making code modifications.
Understanding Decentralized Applications (dApps)
A web app such as Uber or Twitter runs on a computer system that is owned and operated by a company that has authority over the app and its workings. No matter how many users there are, the backend is controlled by the company.
DApps can run on a P2P network or a blockchain network. For example, BitTorrent, Tor, and Popcorn Time are applications that run on computers that are part of a P2P network, which allows multiple participants to consume content, feed, or seed content.
dApps run on a blockchain network in a public, open-source, decentralized environment and are free from control and interference by any single authority. For example, a developer can create a Twitter-like dApp and put it on a blockchain where any user can publish messages. Once posted, no one—not even the app creators—can delete the messages.
dApp Uses
dApps have been developed to decentralize a range of functions and applications and eliminate intermediaries. Examples include self-executing financial contracts, multi-user games, and social media platforms.
DApps have also been developed to enable secure, blockchain-based voting and governance. DApps can even be integrated into web browsers to function as plugins that help serve ads, track user behavior, or solicit crypto donations.
Some examples of practical uses for dApps include:
- Financial services: dApps can be used to facilitate peer-to-peer financial transactions, such as the exchange of currencies or the transfer of assets.
- Supply chain management: dApps can be used to track the movement of goods through a supply chain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Identity verification: dApps can be used to securely store and verify identity information, such as for voter rolls or passport applications.
- Real estate: dApps can be used to facilitate the buying and selling of real estate directly between buyer and seller, as well as the tracking of property ownership and related documentation such as deeds.
- Healthcare: dApps can be used to store and track healthcare records, as well as to facilitate the communication and collaboration of healthcare professionals.
- Education: dApps can be used to create decentralized learning platforms, allowing students and teachers to interact and collaborate directly without the need for intermediaries.
- Social media: dApps can be used to create decentralized social media platforms, allowing users to interact and share content without the need for a central authority.
- Predictive markets: dApps can be used to create decentralized platforms for predictive markets, allowing users to make predictions on a variety of topics and potentially earn rewards for accurate predictions.
dApp Scams
Scams have been perpetrated through dApps. Ponzi schemes, in which early investors are paid using the investments of more recent investors to create the appearance of big profits, have been known to occur on dApps.
Fake initial coin offerings (ICOs) have been used to raise funds for the development of a new cryptocurrency or dApp that the fundraisers have no intention of creating.
Phishing attacks, which use fake websites or emails to trick people into revealing sensitive information, have been seen on dApps.
In addition, some dApps have been used to distribute malware or viruses, which can compromise users’ devices and steal sensitive information.
It is important for users to be cautious and do their due diligence when interacting with dApps, as the decentralized nature of these applications can make it difficult to track or hold perpetrators accountable.
Industry analytics group DappRadar found that there were a record 312 hacks and vulnerabilities affecting dApps in 2022, leading to losses of around $48 billion.
Advantages and Disadvantages of dApps
Advantages
Many of the advantages of dApps center around the program’s ability to safeguard user privacy. With decentralized apps, users do not need to submit their personal information to use the function the app provides. DApps use smart contracts to complete the transaction between two anonymous parties without the need to rely on a central authority.
Free speech proponents point out that dApps can be developed as alternative social media platforms. A decentralized social media platform is resistant to censorship because no single participant on the blockchain can delete or block messages.
Ethereum is a flexible platform for creating new dApps, providing the infrastructure needed for developers to focus their efforts on finding innovative uses for digital applications. This could enable the rapid deployment of dApps in a number of industries including banking and finance, gaming, social media, and online shopping.
Fast Fact
American cryptographer and computer scientist Nick Szabo introduced the term “smart contract” in 1996 as a graduate student at the University of Washington.
Disadvantages
The use of dApps is still in the early stages, and thus it is experimental and prone to certain problems and unknowns. There are questions as to whether the applications will be able to scale effectively. There are concerns that an app that requires significant computations will overload a network, causing network congestion.
The ability to develop a user-friendly interface is another concern. Most users of apps developed by traditional centralized institutions have an ease-of-use expectation that encourages them to use and interact with the app. Getting people to transition to dApps will require developers to create an end-user experience and level of performance that rivals popular and established programs.
The challenge of doing code modifications is another limitation of dApps. Once deployed, a dApp is likely to need ongoing changes to make enhancements or correct bugs or security risks. According to Ethereum, it can be challenging for developers to make needed updates to dApps because the data and code published to the blockchain are hard to modify.
Pros
- Promotes user privacy
- Resists censorship
- Flexible platform enables dApp development
Cons
- Experimental, may not be able to scale
- Challenges in developing a user-friendly interface
- Difficult to make needed code modifications
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Ethereum dApps?
These are decentralized applications that are developed using the Ethereum platform and are powered by it. Ethereum dApps use smart contracts for their logic. They are deployed on the Ethereum network and use the platform’s blockchain for data storage.
What Is the Difference Between a Centralized and Decentralized App?
A centralized app has a single owner. The application software for a centralized app resides on one or more servers controlled by the owner. As a user, you’ll interact with the app by downloading a copy of the app and then sending and receiving data back and forth from the company’s server.
A decentralized app (also known as a dApp or dapp) operates on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network of computers. Users engage in transactions directly with one another rather than relying on a central authority. The user of a dApp will pay the developer an amount of cryptocurrency to download and use the program’s source code. The source code is known as a smart contract, which allows users to complete transactions without revealing personal information.
What Are Examples of Centralized and Decentralized Apps?
Well-known examples of centralized apps include Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and Netflix. Banks and other financial institutions use centralized apps to give their customers online access to their accounts.
Peepeth, a social network alternative to Twitter, is an example of a decentralized app. Cryptokitties is a dApp game that allows users to buy and sell virtual cats. MakerDAO is a decentralized credit service supporting the stablecoin Dai that allows users to open a collateralized debt position (CDP).
The Bottom Line
Decentralized applications (dApps) are digital applications or programs that run on a decentralized network, rather than a single computer or server. They are built on blockchain technology and use cryptocurrency as a means of exchange. dApps are designed to be open-source, transparent, and resistant to censorship, allowing users to interact directly with the application without intermediaries. They have the potential to disrupt traditional industries by allowing for peer-to-peer interactions and transactions without a central authority.